浙大数据结构的编程题——Root of AVL Tree
数据结构-Root of AVL Tree
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
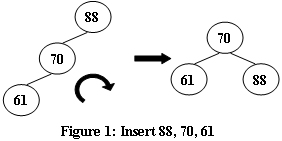
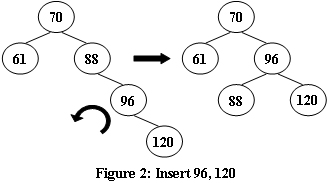
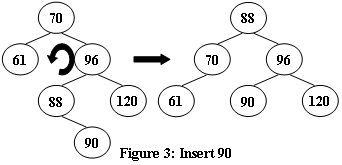
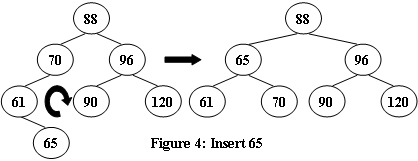
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
思路
本题主要分为两部分内容,一是插入结点,二是检查结点插入后树是否平衡,若不平衡,则通过LL、RR、LR、RL旋转使树重新平衡。
插入结点
此处可以参考是否同一颗二叉搜索树这题的思路与code.
检查结点
检查结点在插入之后,插入完成时,程序递归返回,顺势检查返回路径是否有失衡问题,即左右子树高度相差绝对值为2的情况。 然后判断失衡情况的类型:
- 插入结点在发现失衡的结点的左子树的左侧 -> LL旋转
- 插入结点在发现失衡的结点的左子树的右侧 -> LR旋转
- 插入结点在发现失衡的结点的右子树的左侧 -> RL旋转
- 插入结点在发现失衡的结点的右子树的右侧 -> RR旋转
L也叫左旋,为顺时针旋转。
R同理。
以LR旋转为例,插入结点在发现失衡的结点的左子树的右侧,则发现结点的左子树要先进行一次右旋,再在发现结点进行一次左旋。
RL同理。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <math.h>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define ElementType int
typedef struct AVLNode *Position;
typedef Position AVLTree; /* AVL树类型 */
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A);
struct AVLNode {
ElementType Data; /* 结点数据 */
AVLTree Left; /* 指向左子树 */
AVLTree Right; /* 指向右子树 */
int Height; /* 树高 */
};
int Max(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int GetHeight(AVLTree T) {
if(T)
return T->Height;
else
return -1;
}
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A)
{ /* 注意:A必须有一个左子结点B */
/* 将A与B做左单旋,更新A与B的高度,返回新的根结点B */
AVLTree B = A->Left;
A->Left = B->Right;
B->Right = A;
A->Height = Max(GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right)) + 1;
B->Height = Max(GetHeight(B->Left), A->Height) + 1;
return B;
}
AVLTree SingleRightRotation(AVLTree A)
{
//右单旋
AVLTree B = A->Right;
A->Right = B->Left;
B->Left = A;
A->Height = Max(GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right)) + 1;
B->Height = Max(GetHeight(B->Left), GetHeight(B->Right)) + 1;
return B;
}
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree A)
{ /* 注意:A必须有一个左子结点B,且B必须有一个右子结点C */
/* 将A、B与C做两次单旋,返回新的根结点C */
/* 将B与C做右单旋,C被返回 */
A->Left = SingleRightRotation(A->Left);
/* 将A与C做左单旋,C被返回 */
return SingleLeftRotation(A);
}
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree A)
{
//插入结点在发现不平衡的结点的右子树的左侧
/* 将B与C做左单旋,C被返回 */
A->Right = SingleLeftRotation(A->Right);
/* 将A与C做左单旋,C被返回 */
return SingleRightRotation(A);
}
/*************************************/
/* 对称的右单旋与右-左双旋请自己实现 */
/*************************************/
AVLTree Insert(AVLTree T, ElementType X)
{ /* 将X插入AVL树T中,并且返回调整后的AVL树 */
if (!T) { /* 若插入空树,则新建包含一个结点的树 */
T = (AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct AVLNode));
T->Data = X;
T->Height = 0;
T->Left = T->Right = NULL;
} /* if (插入空树) 结束 */
else if (X < T->Data) {
/* 插入T的左子树 */
T->Left = Insert(T->Left, X);
//先插入,再检查
/* 如果需要左旋 */
if (GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right) == 2)
if (X < T->Left->Data)
T = SingleLeftRotation(T); /* 左单旋 */
else
T = DoubleLeftRightRotation(T); /* 左-右双旋 */
} /* else if (插入左子树) 结束 */
else if (X > T->Data) {
/* 插入T的右子树 */
T->Right = Insert(T->Right, X);
/* 如果需要右旋 */
if (GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right) == -2)
if (X > T->Right->Data)
T = SingleRightRotation(T); /* 右单旋 */
else
T = DoubleRightLeftRotation(T); /* 右-左双旋 */
} /* else if (插入右子树) 结束 */
/* else X == T->Data,无须插入 */
/* 别忘了更新树高 */
T->Height = Max(GetHeight(T->Left), GetHeight(T->Right)) + 1;
return T;
}
int main() {
//begin: end:
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int N;
ElementType data;
AVLTree T=NULL;
scanf("%d\n", &N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%d", &data);
T = Insert(T, data);
}
if (T)
printf("%d", T->Data);
return 0;
}
